Petroleum
Un article de Vev.
Modèle:Portal Petroleum (Latin Petroleum derived from Greek πέτρα (Latin petra) - rock + έλαιον (Latin oleum) - oil) or crude oil is a naturally occurring liquid found in formations in the Earth consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons (mostly alkanes) of various lengths. The approximate length range is C5H12 to C42H86. The formula to work out how many hydrogen atoms there are compared to the amount of carbons is CnH2n+2. Any shorter hydrocarbons are considered natural gas or natural gas liquids, while long-chain hydrocarbons are more viscous, and the longest chains are paraffin wax. In its naturally occurring form, it may contain other nonmetallic elements such as sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.<ref> Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), by the American Petroleum Institute</ref> It is usually black or dark brown (although it may be yellowish or even greenish) but varies greatly in appearance, depending on its composition. Crude oil may also be found in semi-solid form mixed with sand, as in the Athabasca oil sands in Canada, where it may be referred to as crude bitumen.
Petroleum is used mostly, by volume, for producing fuel oil and gasoline (petrol), both important "primary energy" sources. <ref>IEA Key World Energy Statistics</ref> 84% by volume of the hydrocarbons present in petroleum is converted into energy-rich fuels (petroleum-based fuels), including gasoline, diesel, jet, heating, and other fuel oils, and liquefied petroleum gas. <ref>"Crude oil is made into different fuels"</ref>
Due to its high energy density, easy transportability and relative abundance, it has become the world's most important source of energy since the mid-1950s. Petroleum is also the raw material for many chemical products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, and plastics; the 16% not used for energy production is converted into these other materials.
Petroleum is found in porous rock formations in the upper strata of some areas of the Earth's crust. There is also petroleum in oil sands (tar sands). Known reserves of petroleum are typically estimated at around 140 km³ (1.2 trillion barrels) without oil sands <ref>EIA reserves estimates</ref>, or 440 km³ (3.74 trillion barrels) with oil sands <ref> CERA report on total world oil</ref>. However, oil production from oil sands is currently severely limited. Consumption is currently around 84 million barrels per day, or 3.6 km³ per year. Because of reservoir engineering difficulties, recoverable oil reserves are significantly less than total oil-in-place. At current consumption levels, and assuming that oil will be consumed only from reservoirs, known reserves would be gone around 2039, potentially leading to a global energy crisis. However, this ignores any new discoveries, rapidly increasing consumption in China, India, and other developing nations; using oil sands, using synthetic petroleum, and other factors which may extend or reduce this estimate.
Formation
Chemistry
Petroleum is a mixture of a very large number of different hydrocarbons ; the most commonly found molecules are alkanes (linear or branched), cycloalkanes, aromatic, or more complicated like asphaltenes. Each petroleum has a unique mix of molecules, which define its physical and chemical properties, like color and viscosity. These different molecules are separated by fractional distillation at an oil refinery to produce gasoline, jet fuel, kerosene, and other hydrocarbons. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2. For example 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane), widely used in gasoline, has a chemical formula of C8H18 and it reacts with oxygen exothermically:<ref>Heat of Combustion of Fuels</ref>
- <math>2\mathrm{C}_8 \mathrm{H}_{18
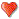 } + 25\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \; 16\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)} + 18\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{
} + 25\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \; 16\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)} + 18\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{ } + 10.86 \ \mathrm{MJ}</math>
} + 10.86 \ \mathrm{MJ}</math>
Incomplete combustion of petroleum or gasoline results in production of potentially toxic byproducts. Too little oxygen results in carbon monoxide. Combustion in air (which contains mostly nitrogen) results in nitric oxides. For example:
- <math>\mathrm{C}_8 \mathrm{H}_{18
 } + 12.5\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} + \mathrm{N}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \; 6\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)} + 2\mathrm{CO}_{(g)} +2\mathrm{NO}_{(g)} + 9\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{
} + 12.5\mathrm{O}_{2(g)} + \mathrm{N}_{2(g)} \rightarrow \; 6\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)} + 2\mathrm{CO}_{(g)} +2\mathrm{NO}_{(g)} + 9\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_{ } + \text{heat}</math>
} + \text{heat}</math>
Formation of petroleum occurs from kerogen pyrolysis, in a variety of mostly endothermic reactions at high temperature and/or pressure. <ref>Petroleum Study</ref>
Biogenic theory
Most geologists view crude oil and natural gas as the product of compression and heating of ancient organic materials over geological time. Oil is formed from the preserved remains of prehistoric zooplankton and algae which have been settled to the sea (or lake) bottom in large quantities under anoxic conditions. Terrestrial plants, on the other hand, tend to form coal. Over geological time this organic matter, mixed with mud, is buried under heavy layers of sediment. The resulting high levels of heat and pressure cause the organic matter to chemically change during diagenesis, first into a waxy material known as kerogen which is found in various oil shales around the world, and then with more heat into liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons in a process known as catagenesis.
Geologists often refer to an "oil window" which is the temperature range that oil forms in—below the minimum temperature oil remains trapped in the form of kerogen, and above the maximum temperature the oil is converted to natural gas through the process of thermal cracking. Though this happens at different depths in different locations around the world, a 'typical' depth for the oil window might be 4–6 km. Note that even if oil is formed at extreme depths, it may be trapped at much shallower depths, even if it is not formed there (the Athabasca Oil Sands is one example).
Because most hydrocarbons are lighter than rock or water, these often migrate upward through adjacent rock layers until they either reach the surface or become trapped beneath impermeable rocks, within porous rocks called reservoirs. However, the process is not straightforward since it is influenced by underground water flows, and oil may migrate hundreds of kilometres horizontally or even short distances downward before becoming trapped in a reservoir. Concentration of hydrocarbons in a trap forms an oil field, from which the liquid can be extracted by drilling and pumping.
Three conditions must be present for oil reservoirs to form: first, a source rock rich in organic material buried deep enough for subterranean heat to cook it into oil; second, a porous and permeable reservoir rock for it to accumulate in; and last a cap rock (seal) or other mechanism that prevents it from escaping to the surface. Within these reservoirs fluids will typically organize themselves like a three-layer cake with a layer of water below the oil layer and a layer of gas above it, although the different layers vary in size between reservoirs.
The vast majority of oil that has been produced by the earth has long ago escaped to the surface and been biodegraded by oil-eating bacteria. Oil companies are looking for the small fraction that has been trapped by this rare combination of circumstances. Oil sands are reservoirs of partially biodegraded oil still in the process of escaping, but contain so much migrating oil that, although most of it has escaped, vast amounts are still present - more than can be found in conventional oil reservoirs. On the other hand, oil shales are source rocks that have never been buried deep enough to convert their trapped kerogen into oil.
The reactions that produce oil and natural gas are often modeled as first order breakdown reactions, where kerogen is broken down to oil and natural gas by a set of parallel reactions, and oil eventually breaks down to natural gas by another set of reactions. The first set was originally patented in 1694 under British Crown Patent No. 330 covering,
"a way to extract and make great quantityes of pitch, tarr, and oyle out of a sort of stone."
The latter set is regularly used in petrochemical plants and oil refineries.
Abiogenic theory
The idea of abiogenic petroleum origin was championed in the Western world by astronomer Thomas Gold based on thoughts from Russia, mainly on studies of Nikolai Kudryavtsev. The idea proposes that hydrocarbons of purely geological origin exist in the planet. Hydrocarbons are less dense than aqueous pore fluids, and are proposed to migrate upward through deep fracture networks. Thermophilic, rock-dwelling microbial life-forms are proposed to be in part responsible for the biomarkers found in petroleum.
This theory is a minority opinion, especially amongst Western geologists; no Western oil companies are currently known to explore for oil based on this theory, although Russia is known to have applied this theory with some success.[citation needed]
Classification
The oil industry classifies "crude" by the location of its origin (e.g., "West Texas Intermediate, WTI" or "Brent") and often by its relative weight or viscosity ("light", "intermediate" or "heavy"); refiners may also refer to it as "sweet," which means it contains relatively little sulfur, or as "sour," which means it contains substantial amounts of sulfur and requires more refining in order to meet current product specifications. Each crude oil has unique molecular characteristics which are understood by the use of crude oil assay analysis in petroleum laboratories.
Barrels from an area in which the crude oil's molecular characteristics have been determined and the oil has been classified are used as pricing references throughout the world. These references are known as Crude oil benchmarks:
- Brent Crude, comprising 15 oils from fields in the Brent and Ninian systems in the East Shetland Basin of the North Sea. The oil is landed at Sullom Voe terminal in the Shetlands. Oil production from Europe, Africa and Middle Eastern oil flowing West tends to be priced off the price of this oil, which forms a benchmark.
- West Texas Intermediate (WTI) for North American oil.
- Dubai, used as benchmark for Middle East oil flowing to the Asia-Pacific region.
- Tapis (from Malaysia, used as a reference for light Far East oil)
- Minas (from Indonesia, used as a reference for heavy Far East oil)
- The OPEC Reference Basket, a weighted average of oil blends from various OPEC (The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) countries.
Petroleum industry
The main activities of the petroleum industry are
- Exploration
- Production
- Processing (refining)
- Marketing and distribution
Petroleum exploration
Extraction
The most common method of obtaining petroleum is extracting it from oil wells found in oil fields. With improved technologies and higher demand for hydrocarbons various methods are applied in petroleum exploration and development to optimize the recovery of oil and gas (Enhanced Oil Recovery, EOR). Primary recovery methods are used to extract oil that is brought to the surface by underground pressure, and can generally recover about 20% of the oil present. The natural pressure can come from several different sources; where it is provided by an underlying water layer it is called a water drive reservoir and where it is from the gas cap above it is called gas drive. After the reservoir pressure has depleted to the point that the oil is no longer brought to the surface, secondary recovery methods draw another 5 to 10% of the oil in the well to the surface. In a water drive oil field, water can be injected into the water layer below the oil, and in a gas drive field it can be injected into the gas cap above to repressurize the reservoir. Finally, when secondary oil recovery methods are no longer viable, tertiary recovery methods reduce the viscosity of the oil in order to bring more to the surface. These may involve the injection of heat, vapor, surfactants, solvents, or miscible gases as in carbon dioxide flooding.
Alternative methods
During the oil price increases of 2004-2007, alternatives methods of producing oil gained importance. The most widely known alternatives involve extracting oil from sources such as oil shale or tar sands. These resources exist in large quantities; however, extracting the oil at low cost without excessively harming the environment remains a challenge.
It is also possible to chemically transform methane or coal into the various hydrocarbons found in oil. The best-known such method is the Fischer-Tropsch process. It was a concept pioneered in Nazi Germany when imports of petroleum were restricted due to war and Germany found a method to extract oil from coal. It was known as Ersatz (English:"substitute") oil, and accounted for nearly half the total oil used in WWII by Germany. However, the process was used only as a last resort as naturally occurring oil was much cheaper. As crude oil prices increase, the cost of coal to oil conversion becomes comparatively cheaper. The method involves converting high ash coal into synthetic oil in a multi-stage process. Ideally, a ton of coal produces nearly 200 liters (1.25 bbl, 52 US gallons) of crude, with by-products including tar.[citation needed]
Currently, two companies have commercialised their Fischer-Tropsch technology. Shell in Bintulu, Malaysia, uses natural gas as a feedstock, and produces primarily low-sulfur diesel fuels. <ref>Shell Middle Distillate Synthesis Malaysia</ref> Sasol <ref>Sasol corporate website</ref> in South Africa uses coal as a feedstock, and produces a variety of synthetic petroleum products.
The process is today used in South Africa to produce most of the country's diesel fuel from coal by the company Sasol. The process was used in South Africa to meet its energy needs during its isolation under Apartheid. This process produces low sulfur diesel fuel ; it also is an increased threat to environment, as it produces large amounts of greenhouse gases.
An alternative method of converting coal into petroleum is the Karrick process, which was pioneered in the 1930s in the United States. It uses high temperatures in the absence of ambient air, to distill the short-chain hydrocarbons of petroleum out of coal.
More recently explored is thermal depolymerization (TDP), a process for the reduction of complex organic materials into light crude oil. Using pressure and heat, long chain polymers of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon decompose into short-chain petroleum hydrocarbons. This mimics the natural geological processes thought to be involved in the production of fossil fuels. In theory, TDP can convert any organic waste into petroleum.
Processing
History
Petroleum, in some form or other, is not a substance new in the world's history. More than four thousand years ago, according to Herodotus and confirmed by Diodorus Siculus, asphalt was employed in the construction of the walls and towers of Babylon; there were oil pits near Ardericca (near Babylon), and a pitch spring on Zacynthus.<ref name=EB1911>Modèle:1911</ref> Great quantities of it were found on the banks of the river Issus, one of the tributaries of the Euphrates. Ancient Persian tablets indicate the medicinal and lighting uses of petroleum in the upper levels of their society.
The earliest known oil wells were drilled in China in 347 CE or earlier. They had depths of up to about Modèle:Formatnum:800 feet ({{formatnum:{{rnd/+|800 *0.3048/1|0 |Modèle:Rnd/00}}}} m) and were drilled using bits attached to bamboo poles.<ref>ASTM timeline of Oil</ref> The oil was burned to evaporate brine and produce salt. By the 10th century, extensive bamboo pipelines connected oil wells with salt springs. The ancient records of China and Japan are said to contain many allusions to the use of natural gas for lighting and heating. Petroleum was known as burning water in Japan in the 7th century. <ref name=EB1911 />
The Middle East petroleum industry was established by the 8th century, when the streets of the newly constructed Baghdad were paved with tar, derived from easily accessible petroleum from natural fields in the region. In the 9th century, oil fields were exploited in the area around modern Baku, Azerbaijan, to produce naphtha. These fields were described by the geographer Masudi in the 10th century, and by Marco Polo in the 13th century, who described the output of those wells as hundreds of shiploads. Petroleum was distilled by Persian chemist al-Razi in the 9th century, producing chemicals such as kerosene in the al-ambiq (alembic). <ref name=Ajram> Modèle:Cite book </ref> (See also: Alchemy (Islam), Islamic science, and Timeline of science and technology in the Islamic world.)
The earliest mention of American petroleum occurs in Sir Walter Raleigh's account of the Trinidad Pitch Lake in 1595; whilst thirty-seven years later, the account of a visit of a Franciscan, Joseph de la Roche d'Allion, to the oil springs of New York was published in Sagard's Histoire du Canada. A Russian traveller, Peter Kalm, in his work on America published in 1748 showed on a map the oil springs of Pennsylvania. <ref name=EB1911 />
In 1711 the Greek physician Eyrini d’Eyrinis discovered asphalt at Val-de-Travers, (Neuchâtel). He established a bitumen mine de la Presta there in 1719 that operated until 1986. <ref>[1]</ref><ref>Le bitume et la mine de la Presta (Suisse), Jacques Lapaire, Mineraux et Fossiles No 315</ref>
Oil sands were mined from 1745 in Merkwiller-Pechelbronn, Alsace under the direction of Louis Pierre Ancillon de la Sablonnière, by special appointement of Louis XV.<ref name=Pechelbronn> History of Pechelbronn oil</ref> The Pechelbronn oil field was active until 1970, and was the birth place of companies like Antar and Schlumberger. The first modern refinery was built there in 1857.<ref name=Pechelbronn/>
The modern history of petroleum began in 1846 with the discovery of the process of refining kerosene from coal by Nova Scotian Abraham Pineo Gesner.
Ignacy Łukasiewicz improved Gesner's method to develop a means of refining kerosene from the more readily available "rock oil" ("petr-oleum") seeps in 1852 and the first rock oil mine was built in Bóbrka, near Krosno in Galicia in the following year. These discoveries rapidly spread around the world, and Meerzoeff built the first Russian refinery in the mature oil fields at Baku in 1861. At that time Baku produced about 90% of the world's oil.
The first commercial oil well drilled in North America was in Oil Springs, Ontario, Canada in 1858, dug by James Miller Williams. The US petroleum industry began with Edwin Drake's drilling of a Modèle:Formatnum:69-foot ({{formatnum:{{rnd/+|69*0.3048/1|0|Modèle:Rnd/00}}}} m) oil well in 1859, on Oil Creek near Titusville, Pennsylvania, for the Seneca Oil Company (originally yielding 25 barrels a day, by the end of the year output was at the rate of 15 barrels). The industry grew slowly in the 1800s, driven by the demand for kerosene and oil lamps. It became a major national concern in the early part of the 20th century; the introduction of the internal combustion engine provided a demand that has largely sustained the industry to this day. Early "local" finds like those in Pennsylvania and Ontario were quickly outpaced by demand, leading to "oil booms" in Texas, Oklahoma, and California.
Early production of crude petroleum in the United States: <ref name=EB1911 />
- 1859: Modèle:Bbl to t
- 1869: Modèle:Bbl to t
- 1879: Modèle:Bbl to t
- 1889: Modèle:Bbl to t
- 1899: Modèle:Bbl to t
- 1906: 126,493,936 barrels (~21,600,000 t)
By 1910, significant oil fields had been discovered in Canada (specifically, in the province of Ontario), the Dutch East Indies (1885, in Sumatra), Iran (1908, in Masjed Soleiman), Peru, Venezuela, and Mexico, and were being developed at an industrial level.
Even until the mid-1950s, coal was still the world's foremost fuel, but oil quickly took over. Following the 1973 energy crisis and the 1979 energy crisis, there was significant media coverage of oil supply levels. This brought to light the concern that oil is a limited resource that will eventually run out, at least as an economically viable energy source. At the time, the most common and popular predictions were always quite dire, and when they did not come true, many dismissed all such discussion. The future of petroleum as a fuel remains somewhat controversial. USA Today news (2004) reports that there are 40 years of petroleum left in the ground. Some[citation needed] argue that because the total amount of petroleum is finite, the dire predictions of the 1970s have merely been postponed. Others[citation needed] claim that technology will continue to allow for the production of cheap hydrocarbons and that the earth has vast sources of unconventional petroleum reserves in the form of tar sands, bitumen fields and oil shale that will allow for petroleum use to continue in the future, with both the Canadian tar sands and United States shale oil deposits representing potential reserves matching existing liquid petroleum deposits worldwide.
Today, about 90% of vehicular fuel needs are met by oil. Petroleum also makes up 40% of total energy consumption in the United States, but is responsible for only 2% of electricity generation. Petroleum's worth as a portable, dense energy source powering the vast majority of vehicles and as the base of many industrial chemicals makes it one of the world's most important commodities. Access to it was a major factor in several military conflicts including World War II and the Persian Gulf Wars of the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. The top three oil producing countries are Saudi Arabia, Russia, and the United States. About 80% of the world's readily accessible reserves are located in the Middle East, with 62.5% coming from the Arab 5: Saudi Arabia (12.5%), UAE, Iraq, Qatar and Kuwait. However, with today's oil prices, Venezuela has larger reserves than Saudi Arabia due to crude reserves derived from bitumen.
Uses
The chemical structure of petroleum is composed of hydrocarbon chains of different lengths. Because of this, petroleum may be taken to oil refineries and the hydrocarbon chemicals separated by distillation and treated by other chemical processes, to be used for a variety of purposes. See Petroleum products.
Fuels
- Ethane and other short-chain alkanes which are used as fuel
- Diesel fuel (petrodiesel)
- Fuel oils
- Gasoline
- Jet fuel
- Kerosene
- Liquid petroleum gas (LPG)
- Natural gas
Generally used in transportation, power plants and heating.
Petroleum vehicles are internal combustion engine vehicles.
Other derivatives
Certain types of resultant hydrocarbons may be mixed with other non-hydrocarbons, to create other end products:
- Alkenes (olefins) which can be manufactured into plastics or other compounds
- Lubricants (produces light machine oils, motor oils, and greases, adding viscosity stabilizers as required).
- Wax, used in the packaging of frozen foods, among others.
- Sulfur or Sulfuric acid. These are a useful industrial materials. Sulfuric acid is usually prepared as the acid precursor oleum, a byproduct of sulfur removal from fuels.
- Bulk tar.
- Asphalt
- Petroleum coke, used in speciality carbon products or as solid fuel.
- Paraffin wax
- Aromatic petrochemicals to be used as precursors in other chemical production.
Consumption statistics
2004 U.S. government predictions for oil production other than in OPEC and the former Soviet Union |
Environmental effects
The presence of oil has significant social and environmental impacts, from accidents and routine activities such as seismic exploration, drilling, and generation of polluting wastes not produced by other alternative energies.
Extraction
Oil extraction is costly and sometimes environmentally damaging, although Dr. John Hunt of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution pointed out in a 1981 paper that over 70% of the reserves in the world are associated with visible macroseepages, and many oil fields are found due to natural leaks. Offshore exploration and extraction of oil disturbs the surrounding marine environment. <ref>Waste discharges during the offshore oil and gas activity by Stanislave Patin</ref> Extraction may involve dredging, which stirs up the seabed, killing the sea plants that marine creatures need to survive. But at the same time, offshore oil platforms also form micro-habitats for marine creatures.
Oil spills
Crude oil and refined fuel spills from tanker ship accidents have damaged natural ecosystems in Alaska, the Galapagos Islands, France and many other places and times in Spain (i.e. Ibiza).
The quantity of oil spilled during accidents has ranged from a few hundred tons to several hundred thousand tons (Atlantic Empress, Amoco Cadiz...). Smaller spills have already proven to have a great impact on ecosystems, such as the Exxon Valdez oil spill
Oil spills at sea are generally much more damaging than those on land, since they can spread for hundreds of nautical miles in a thin oil slick which can cover beaches with a thin coating of oil. This can kill sea birds, mammals, shellfish and other organisms it coats. Oil spills on land are more readily containable if a makeshift earth dam can be rapidly bulldozed around the spill site before most of the oil escapes, and land animals can avoid the oil more easily.
Control of oil spills is difficult, requires ad hoc methods, and often a large amount of manpower (picture). The dropping of bombs and incendiary devices from aircraft on the Torrey Canyon wreck got poor results<ref>Torrey Canyon bombing by the Navy and RAF</ref> ; modern techniques would include pumping the oil from the wreck, like in the Prestige oil spill or the Erika oil spill<ref>Pumping of the Erika cargo</ref>.
Global warming
Burning oil releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, which has been argued to contribute to global warming. Per watt, oil produces 15% less CO2 than coal, but 30% more than natural gas[citation needed]. However, the unique role of oil as the main source of transportation fuel makes reducing its CO2 emissions a difficult problem. While large power plants can, in theory, eliminate their CO2 emissions by techniques such as carbon sequestering or even use them to increase oil production through enhanced oil recovery techniques, these amelioration strategies do not generally work for individual vehicles
Whales
It has been argued that the advent of petroleum-refined kerosene saved the great cetaceans from extinction by providing a cheap substitute for whale oil, thus eliminating the economic imperative for whaling.<ref>How Capitalism Saved the Whales by James S. Robbins, The Freeman, August, 1992.</ref>
Alternatives to petroleum
Alternatives to petroleum-based vehicle fuels
The term alternative propulsion or "alternative methods of propulsion" includes both:
- alternative fuels used in standard or modified internal combustion engines (i.e. combustion hydrogen or biofuels).
- propulsion systems not based on internal combustion, such as those based on electricity (for example, all-electric or hybrid vehicles), compressed air, or fuel cells (i.e. hydrogen fuel cells).
Nowadays, cars can be classified between the next main groups:
- Petro-cars, this is, only use petroleum and biofuels (biodiesel and biobutanol).
- Hybrid vehicle and plug-in hybrids, that use petroleum and other source, generally, electricity.
- Petrofree car, that can not use petroleum, like electric cars, hydrogen vehicles...
Future of petroleum production
Hubbert peak theory
The Hubbert peak theory (also known as peak oil) posits that future world petroleum production will eventually peak and then decline at a similar rate to the rate of increase before the peak as these reserves are exhausted. It also suggests a method to calculate the timing of this peak, based on past production rates, past discovery rates, and proven oil reserves.
Controversy surrounds the theory for numerous reasons. Past predictions regarding the timing of the global peak have failed, causing a number of observers to disregard the theory. Further, predictions regarding the timing of the peak are highly dependent on the past production and discovery data used in the calculation.
Proponents of peak oil theory also refer as an example, that when any given oil well produces oil in similar volumes to the amount of water used to obtain the oil, it tends to produce less oil afterwards, leading to the relatively quick exhaustion and/or commercial inviability of the well in question.
The theory is applied to both individual regions and the world as a whole. Hubbert's prediction for when US oil production would peak turned out to be correct, and after this occurred in 1971 - causing the US to lose its excess production capacity - OPEC was finally able to manipulate oil prices, which led to the 1973 oil crisis. Since then, most other countries have also peaked: the United Kingdom's North Sea, for example in the late 1990s. China has confirmed that two of its largest producing regions are in decline, and Mexico's national oil company, Pemex, has announced that Cantarell Field, one of the world's largest offshore fields, was expected to peak in 2006, and then decline 14% per annum.
It is difficult to predict the oil peak in any given region, due to the lack of transparency in accounting of global oil reserves.<ref>New study raises doubts about Saudi oil reserves</ref> Based on available production data, proponents have previously predicted the peak for the world to be in years 1989, 1995, or 1995-2000. Some of these predictions date from before the recession of the early 1980s, and the consequent reduction in global consumption, the effect of which was to delay the date of any peak by several years. A new prediction by Goldman Sachs picks 2007 for oil and some time later for natural gas.[citation needed] Just as the 1971 U.S. peak in oil production was only clearly recognized after the fact, a peak in world production will be difficult to discern until production clearly drops off.
Many proponents of the Hubbert peak theory argue that the production peak is imminent. The year 2005 saw a dramatic fall in announced new oil projects coming to production from 2008 onwards - in order to avoid the peak, these new projects would have to not only make up for the depletion of current fields, but increase total production annually to meet increasing demand.
The year 2005 also saw substantial increases in oil prices due to a number of circumstances, including war and political instability. Oil prices rose to new highs. Analysts such as Kenneth Deffeyes <ref> Modèle:Cite book </ref> argue that these price increases indicate a general lack of spare capacity, and the price fluctuations can be interpreted as a sign that peak oil is imminent.
Pricing
Petroleum by country
Consumption rates
There are two main ways to measure the oil consumption rates of countries: by population or by GDP (gross domestic product). This metric is important in the global debate over oil consumption/energy consumption/climate change because it takes social and economic considerations into account when scoring countries on their oil consumption/energy consumption/climate change goals. Nations such as China and India with large populations tend to promote the use of population based metrics, while nations with large economies such as the United States would tend to promote the GDP based metric.[citation needed]
| Selected Nations | GDP by consumption (US dollar/barrel/day) |
|---|---|
| Switzerland | 3.75 |
| United Kingdom | 3.34 |
| Norway | 3.31 |
| Austria | 2.96 |
| France | 2.65 |
| Germany | 2.89 |
| Sweden | 2.71 |
| Italy | 2.57 |
| European Union | 2.52 |
| DRC | 2.4 |
| Japan | 2.34 |
| Australia | 2.21 |
| Spain | 1.96 |
| Bangladesh | 1.93 |
| Poland | 1.87 |
| United States | 1.65 |
| Belgium | 1.59 |
| World | 1.47 |
| Turkey | 1.39 |
| Canada | 1.35 |
| Mexico | 1.07 |
| Ethiopia | 1.04 |
| South Korea | 1.00 |
| Philippines | 1.00 |
| Brazil | 0.99 |
| Taiwan | 0.98 |
| China | 0.94 |
| Nigeria | 0.94 |
| Pakistan | 0.93 |
| Myanmar | 0.89 |
| India | 0.86 |
| Russia | 0.84 |
| Indonesia | 0.71 |
| Vietnam | 0.61 |
| Thailand | 0.53 |
| Saudi Arabia | 0.46 |
| Egypt | 0.41 |
| Singapore | 0.40 |
| Iran | 0.35 |
| Selected Nations | Per capita consumption (barrel/person/year) |
|---|---|
| DRC | 0.13 |
| Ethiopia | 0.37 |
| Bangladesh | 0.57 |
| Myanmar | 0.73 |
| Pakistan | 1.95 |
| Nigeria | 2.17 |
| India | 2.18 |
| Vietnam | 2.70 |
| Philippines | 3.77 |
| Indonesia | 4.63 |
| China | 4.96 |
| Egypt | 7.48 |
| Turkey | 9.85 |
| Brazil | 11.67 |
| Poland | 11.67 |
| World | 12.55 |
| Thailand | 13.86 |
| Russia | 17.66 |
| Mexico | 18.07 |
| Iran | 21.56 |
| European Union | 29.70 |
| United Kingdom | 30.18 |
| Germany | 32.31 |
| France | 32.43 |
| Italy | 32.43 |
| Austria | 34.01 |
| Spain | 35.18 |
| Switzerland | 34.64 |
| Sweden | 34.68 |
| Taiwan | 41.68 |
| Japan | 42.01 |
| Australia | 42.22 |
| South Korea | 43.84 |
| Norway | 52.06 |
| Belgium | 61.52 |
| United States | 68.81 |
| Canada | 69.85 |
| Saudi Arabia | 75.08 |
| Singapore | 178.45 |
(Note: The figure for Singapore is skewed because of its small
population compared with its large oil refining capacity.
Most of this oil is sent to other countries.)
Production
In petroleum industry parlance, production refers to the quantity of crude extracted from reserves, not the literal creation of the product.
In order of amount produced in 2006 in thousand bbl/d and thousand m³/d:
| # | Producing Nation (2006) | (103bbl/d) | (103m3/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saudi Arabia (OPEC) | 10,719 | 1,704 |
| 2 | Russia 1 | 9,668 | 1,537 |
| 3 | United States 1 | 8,367 | 1,330 |
| 4 | Iran (OPEC) | 4,146 | 659 |
| 5 | China | 3,836 | 610 |
| 6 | Mexico 1 | 3,706 | 589 |
| 7 | Canada 2 | 3,289 | 523 |
| 8 | United Arab Emirates (OPEC) | 2,938 | 467 |
| 9 | Venezuela (OPEC) 1 | 2,803 | 446 |
| 10 | Norway 1 | 2,785 | 443 |
| 11 | Kuwait (OPEC) | 2,674 | 425 |
| 12 | Nigeria (OPEC) | 2,443 | 388 |
| 13 | Brazil | 2,163 | 344 |
| 14 | Algeria (OPEC) | 2,122 | 337 |
| 15 | Iraq (OPEC) 3 | 2,008 | 319 |
Source: US Energy Information Administration
1 peak production of conventional oil already passed in this state
2 Although Canadian conventional oil production is declining, total oil production is increasing as oil sands production grows. If oil sands are included, it has the world's second largest oil reserves after Saudi Arabia.
3 Though still a member, Iraq has not been included in production figures since 1998
Export
In order of net exports in 2006 in thousand bbl/d and thousand m³/d:
| # | Exporting Nation (2006) | (103bbl/d) | (103m3/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saudi Arabia (OPEC) | 8,651 | 1,376 |
| 2 | Russia 1 | 6,565 | 1,044 |
| 3 | Norway 1 | 2,542 | 404 |
| 4 | Iran (OPEC) | 2,519 | 401 |
| 5 | United Arab Emirates (OPEC) | 2,515 | 400 |
| 6 | Venezuela (OPEC) 1 | 2,203 | 350 |
| 7 | Kuwait (OPEC) | 2,150 | 342 |
| 8 | Nigeria (OPEC) | 2,146 | 341 |
| 9 | Algeria (OPEC) 1 | 1,847 | 297 |
| 10 | Mexico 1 | 1,676 | 266 |
| 11 | Libya (OPEC) 1 | 1,525 | 242 |
| 12 | Iraq (OPEC) | 1,438 | 229 |
| 13 | Angola (OPEC) | 1,363 | 217 |
| 14 | Kazakhstan | 1,114 | 177 |
| 15 | Canada 2 | 1,071 | 170 |
Source: US Energy Information Administration
1 peak production already passed in this state
2 Canadian statistics are complicated by the fact it is both an importer and exporter of crude oil, and refines large amounts of oil for the U.S. market. It is the leading source of U.S. imports of oil and products, averaging 2.5 MMbbl/d in August 2007. [2].
Total world production/consumption (as of 2005) is approximately 84 million barrels per day.
See also: Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.
Consumption
In order of amount consumed in 2006 in thousand bbl/d and thousand m³/d:
| # | Consuming Nation 2006 | (103bbl/day) | (103m3/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States 1 | 20,588 | 3,273 |
| 2 | China | 7,274 | 1,157 |
| 3 | Japan 2 | 5,222 | 830 |
| 4 | Russia 1 | 3,103 | 493 |
| 5 | Germany 2 | 2,630 | 418 |
| 6 | India 2 | 2,534 | 403 |
| 7 | Canada | 2,218 | 353 |
| 8 | Brazil | 2,183 | 347 |
| 9 | South Korea 2 | 2,157 | 343 |
| 10 | Saudi Arabia (OPEC) | 2,068 | 329 |
| 11 | Mexico 1 | 2,030 | 323 |
| 12 | France 2 | 1,972 | 314 |
| 13 | United Kingdom 1 | 1,816 | 289 |
| 14 | Italy 2 | 1,709 | 272 |
| 15 | Iran (OPEC) | 1,627 | 259 |
Source: US Energy Information Administration
1 peak production of oil already passed in this state
2 This country is not a major oil producer
Import
In order of net imports in 2006 in thousand bbl/d and thousand m³/d:
| # | Importing Nation (2006) | (103bbl/day) | (103m3/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States 1 | 12,220 | 1,943 |
| 2 | Japan | 5,097 | 810 |
| 3 | China 2 | 3,438 | 547 |
| 4 | Germany | 2,483 | 395 |
| 5 | South Korea | 2,150 | 342 |
| 6 | France | 1,893 | 301 |
| 7 | India | 1,687 | 268 |
| 8 | Italy | 1,558 | 248 |
| 9 | Spain | 1,555 | 247 |
| 10 | Taiwan | 942 | 150 |
| 11 | Netherlands | 936 | 149 |
| 12 | Singapore | 787 | 125 |
| 13 | Thailand | 606 | 96 |
| 14 | Turkey | 576 | 92 |
| 15 | Belgium | 546 | 87 |
Source: US Energy Information Administration
1 peak production of oil already passed in this state
2 Major oil producer whose production is still increasing
Non-producing consumers
| # | Consuming Nation | (bbl/day) | (m³/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Japan | 5,578,000 | 886,831 |
| 2 | Germany | 2,677,000 | 425,609 |
| 3 | India | 2,320,000 | 368,851 |
| 4 | South Korea | 2,061,000 | 327,673 |
| 5 | France | 2,060,000 | 327,514 |
| 6 | Italy | 1,874,000 | 297,942 |
| 7 | Spain | 1,537,000 | 244,363 |
| 8 | Netherlands | 946,700 | 150,513 |
Source : CIA World Factbook
With the exception of South Korea, all the nations listed above have some crude oil production, ranging from 3,000 barrels per day for Spain to 689,000 barrels per day for India, but all such production is tiny compared to their consumption. Energy Information Administration
Writers covering the petroleum industry
See also
- List of oil fields
- List of oil-producing states
- List of oil-consuming states
- Partial List of Countries that have already passed their production peak
- List of petroleum companies
- 1990 spike in the price of oil
- Abiogenic petroleum origin
- ANWR (Arctic National Wildlife Refuge)
- Banning of leaded petrol
- Ecodollar
- Energy conservation
- Energy crisis: 1973 energy crisis, 1979 energy crisis
- Eugene Island
- Fossil fuel
- Gas oil ratio
- Global warming
- Greenhouse gases
- Gross domestic product per barrel
- History of the Petroleum Industry
- Hubbert peak
- Future energy development
- Mineral oil
- Nationalization of oil supplies
- Natural gas, another fossil fuel
- Non-conventional oil
- Oil imperialism and nationalization
- Oil phase-out in Sweden
- Oil price increases of 2004-2006
- Oil refinery
- Oil reserves
- Oil supplies
- Oil well
- Olduvai theory (not strictly about oil, but it basically assumes that oil and gas are the only significant energy sources)
- Passive margin
- Platts
- Peak oil
- Petroleum disasters
- Petroleum geology
- Petrodollar
- Petro-free : that does not use or sell petroleum (i.e. petro-free fuel station).
- Petroleum politics
- Predicting the timing of peak oil
- Price of oil
- Renewable energy
- Rosneft
- Soft energy path
- Subsea
- Thermal depolymerization
- Thomas Gold
- World energy resources and consumption
References
External links
- [Petroleum Catégorie Science/Earth_Sciences/Geology/Petroleum] de l’annuaire dmoz.
- Energy Information Administration
- Department of Energy EIA - World supply and consumption
- American Petroleum Institute - the trade association of the US oil industry.Modèle:Link FA
af:Ru-olie ar:نفط an:Petrolio bn:জ্বালানী zh-min-nan:Chio̍h-iû be:Нафта be-x-old:Нафта bs:Gorivo bg:Нефт ca:Petroli cs:Ropa cy:Petroliwm da:Råolie de:Erdöl et:Nafta el:Πετρέλαιο es:Petróleo eo:Nafto eu:Petrolio fa:نفت fr:Pétrole gl:Petróleo ko:석유 hr:Nafta io:Nafto id:Minyak bumi ia:Petroleo is:Hráolía it:Petrolio he:נפט ku:Neft lv:Nafta lt:Nafta ln:Pitɔlɔ́ hu:Kőolaj ms:Petroleum mn:Газрын тос nah:Chiapopohtli nl:Aardolie ja:石油 no:Petroleum nn:Petroleum oc:Petròli pl:Ropa naftowa pt:Petróleo ro:Petrol qu:Allpa wira ru:Нефть simple:Petroleum sk:Ropa sl:Nafta sr:Нафта su:Minyak bumi fi:Maaöljy sv:Petroleum ta:எரிபொருள் th:ปิโตรเลียม vi:Dầu mỏ tr:Petrol uk:Нафта wa:Petrole yi:נאפט bat-smg:Napta zh:石油
Catégories de la page: All articles with unsourced statements | Articles with unsourced statements since September 2007 | Articles with invalid date parameter in template | Articles with unsourced statements since October 2007 | Articles with unsourced statements since December 2007 | Articles with unsourced statements since February 2007 | Lubricants | Oils | Petroleum | Soil contamination | Water pollution | Chemical mixtures | Energy sources
